Questions 28-34 are based on the following passage.
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a sealed, evacuated glass tube with a filament at one end and a fluorescent screen at the other end (see Figure 1). 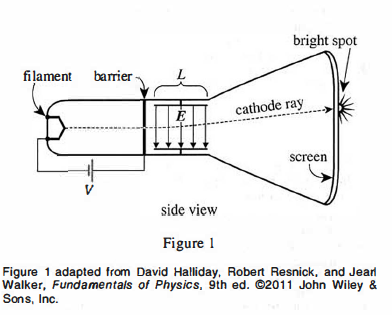
When heated, the filament emits cathode rays that are accelerated by an electric potential, V, toward a barrier having a pinhole. Beyond the barrier are 2 conducting plates, each of length L, that have an electric field, E. between them. (The direction of E can be upward or downward; in Figure 1, it is downward.) Any rays that pass through the pinhole travel through the field and strike the screen, producing a bright spot of visible light.
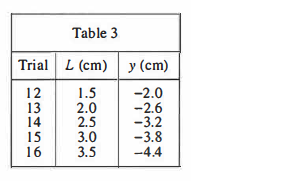
A group of students performed 3 studies on various CRTs, each of which had a ruler taped to the outer surface of the screen (see Figure 2) to measure a spot's vertical location, y (in centimeters, cm). 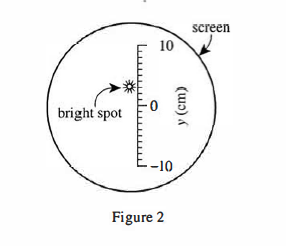
Study 1
The students obtained a CRT having L = 2.5 cm. They set V to 1.0 kilovolt (kV), varied both the direction and the magnitude (in newtons per coulomb, N/C) of E, and recorded the resulting values of y (see Table 1). 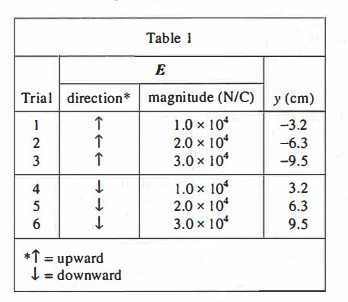
Study 2
Using the CRT from Study 1, the students set the magnitude of E to 1.0 x 10⁴ N/C, varied V, and recorded the resulting values of y (see Table 2). 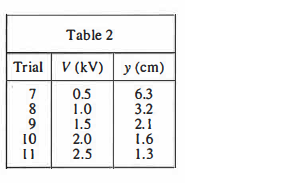
Study 3
The students obtained various CRTs, each having a different L. For each CRT, they set V to 1.0 kV, set the magnitude of E to 1.0 x 10⁴ N/C, and recorded the resulting value of y (see Table 3).